RPA Implementation
What is RPA?
Robotic process automation uses software ‘bots’ to carry out tasks according to a flowchart, following rule-based decisions for a computer-based process with no human interpretation necessary. But too often, one of these 6 common myths of RPA implementation will prevent organizations from making best use of the technology.
Let robots do what they are best at … and let humans do what they are best at.
Pankaj Chowdhry, CEO, FortressIQ
Most organizations have moved past an initial wariness of robotic process automation, to accept its fundamental benefits: saving time, reducing spending, and removing HFT (also known as ‘human finger trouble’) as robots perform certain given tasks more quickly, more accurately, and for longer than any human can.
Bringing RPA online requires a strong clear vision, one that your implementation team will stand for and your stakeholders will buy into. By having involvement, you create commitment. Then, ensure that you provide a human benefit, leading to a customer benefit, resulting in a business benefit.
The first rule of any technology used in a business is that automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency. The second is that automation applied to an inefficient operation will magnify the inefficiency.
Bill Gates, former CEO, Microsoft
6 common myths of RPA implementation
There are many misconceptions surrounding the use of automation. Here are 6 common myths of RPA implementation, and what you should remember instead.
We need an army of bots
RPA can start with just one or two bots and the business can scale up the workforce in accordance with its success. Many companies won’t even need to own a bot, but can make use of Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) technologies.
Bots will take our jobs
The human workforce and its intellectual capacity are far too valuable. In many circumstances, RPA has seen an increase in jobs as teams become more productive causing companies to grow. Bots can remove the burden of certain tasks from a workforce, but this gives businesses the opportunity to upskill and multi skill their staff with the proper training.
Bots are great virtual assistants, owned by your team to do the mundane tasks, leaving the higher-level thinking to us humans. Bots are there to enhance our efficiency and effectiveness, not replace it.
AI bots can do most human tasks
AI can understand natural language, it can learn and recognize images, but it is a long way from replicating human intuition and reasoning. Many bot activities still require routing certain tasks to humans.
Bots don’t make mistakes
Though a bot does exactly what it’s told, if it is programmed incorrectly, it will carry out a task incorrectly a thousand times. Also, certain unforeseen exceptions or bad data inputs could cause the bot to complete the job in the wrong way, or not at all.
RPA means the end of BPM
Before diving into an RPA initiative, it’s vital to capture and analyze your existing processes, using automated process discovery tools and insights from process participants. Only once processes are modelled can you make informed decisions about where automation can best be deployed. Unlike RPA, BPM is not software, but a method to streamline a process. Think of it as a car driving down a road: BPM is building the road to take a specific route; RPA is a self-driven car driving down that same road.
RPA will almost make IT departments redundant
RPA is HEAVILY dependent on the IT team, so much that it’s vital to get IT involved early. Once bots are deployed, you still need to manage them — this is where the concept of Digital Workforce Management becomes extremely important. The bot is merely a virtual employee.
Where can I use RPA technology?
When considering where best to apply RPA technology, there are a few typical criteria that can help to identify RPA candidate tasks:
- No human intuition needed – mundane tasks
- Stable/low variability
- Rule-based
- Manual & Repetitive
- Digitized end-to-end
- Standardized Process
- No pending changes
- High-volume processes
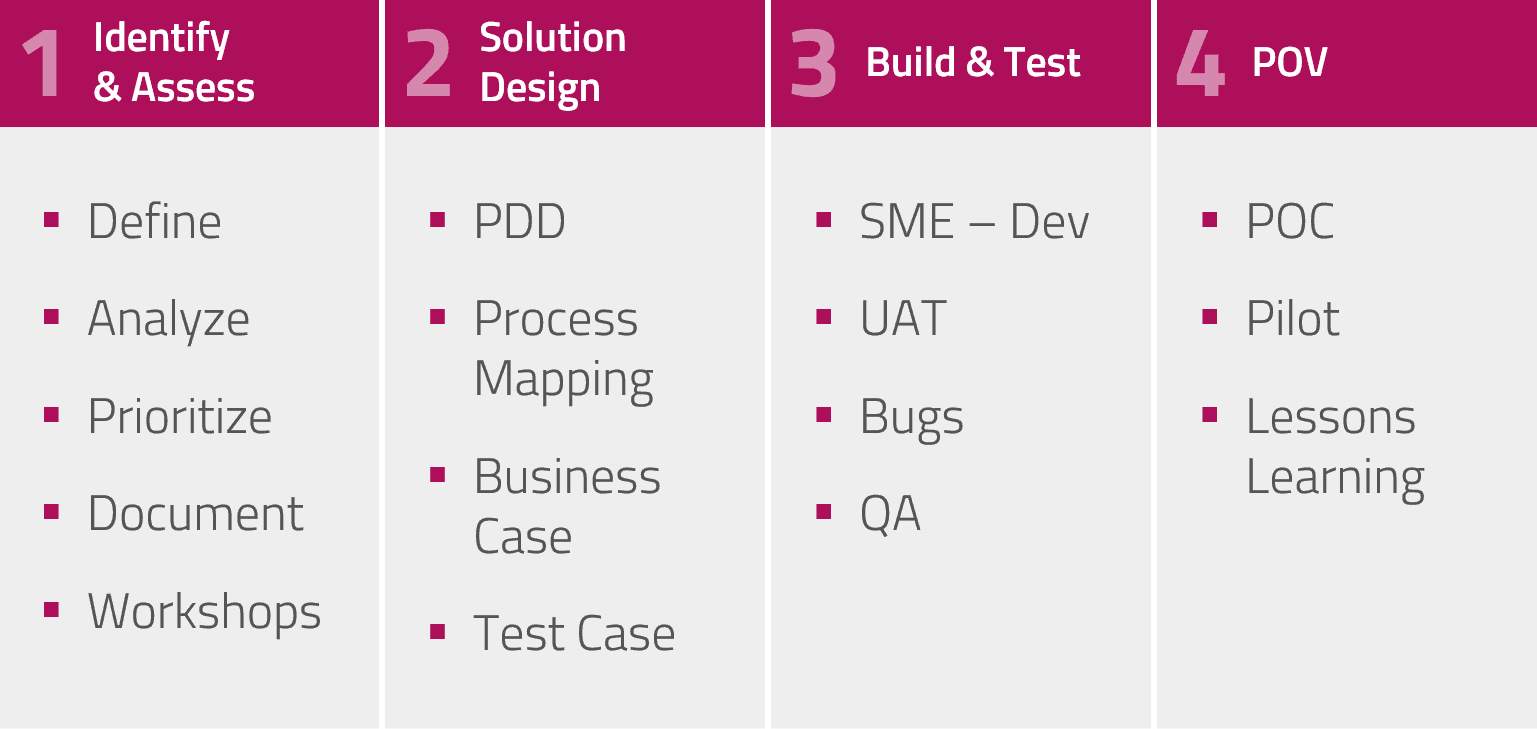
Key steps in implementing RPA
- Identify and assess the process. Is it suitable? Determine the benefits you will gain from automation.
- Get stakeholders together to design the solution and streamline and optimize the process first.
- Hand over to the developer team to build and perform UAT testing.
- Determine through via 'proof of value' whether the automation initiative worked and created benefit.
- Communicate early and frequently throughout the process to keep stakeholders involved and help them stay engaged.
- The proof of value is a big learning experience and by documenting the lessons learned you will frame your RPA implementation for the big event.
The table below shows the sub-tasks and possible tools you can use for the main steps outlined above.
Top benefits of RPA
- Improve job satisfaction
Remove frustrating, mundane, tedious tasks, so you can focus on interesting and value-adding work. - Solve technical issues fast
Remove technical roadblocks and mundane tasks in 2-3 months. - Use your own technology
You decide what problems to solve without waiting for IT to make changes. - 24/7 virtual assistance
Dedicated bots to assist you during the day, or to work for you when you’re at home. - Exceed your targets
Bots cut out mundane tasks, so you can focus on delivering value. - Innovate and stand out
A strong RPA game means you can create more revenue generating services to offer customers & drive business growth. - Analyze with ease
Makes generating reports easier, so you get a comprehensive overview on performance, and can make use of the insights to drive business decisions. - Manage the unexpected
Having a flexible workforce at your fingertips means you can create innovative solutions to spikes in demand or other events.
Aiming for strategic RPA implementation
As you can see from these 6 common myths of RPA implementation, many companies fall into the trap of treating RPA as a tool that simply attaches to their existing systems and processes, with the goal of improving their short-term efficiency. This is the narrowest view of what effective automation can achieve.
Following the quickest and easiest route to implementation, even with the best RPA software in the world, is a tactical solution unlikely to lead to sustainable improvements. The key to lasting success is embracing a strategic, enterprise-level view of RPA, which in turn means taking the time to truly understand the way your organization’s processes function, and then using this information to effectively target your RPA solution.
The winners in today’s competitive market space are organizations who think strategically about the impact processes have on a business. The SAP Signavio Process Transformation Suite gives you the technology you need to get your process landscape in order, before you make a decision on which RPA software you will deploy to automate your processes.
The Suite offers a set of powerful, enterprise-level BPM software solutions, which together serve as the foundation for effective enterprise-level RPA — and other forms of digital transformation as well.

