The power of process mining
Processes are the lifeblood of any business. Whether they are carried out by people, automated or both, most of those processes leave digital traces. Process mining uses these digital traces or event logs to visualize how each process actually functions, in comparison to how the process is intended to function. Process mining helps ‘paint a picture’ of what is really happening in your business.
By mining event logs data — instead of using interviews and estimates — process mining reveals where workarounds, shadow processes, bottlenecks and compliance issues occur and plays a critical role in improving business operations and reducing risks. Learn more about the power of process mining in Your Guide to the Power of Process Mining.
What is process mining?
- The power of process mining
- How has process mining become critical to modern enterprises?
- Why should companies use process mining?
- What can process mining improve?
- How does process mining improve the customer journey?
- When should you use process mining?
- Four steps to launch a successful process mining initiative
Process mining related terms you need to know
Before we dive into some common questions about process mining, let’s define process mining and some related terms:
| Business intelligence | In the context of process mining, business intelligence refers to strategies and technologies that help businesses unlock value through data-driven decisions. |
| Process discovery | The tools and techniques used to define, map and analyze existing processes. This includes process mining and process modeling. |
| Process mining | Analyzing enterprise-level data to uncover how each process actually functions. |
| Process modeling | A means of visualizing processes, such as a process map. Also called business process modeling. |
| Task mining | Analyzing data at the desktop level to gain insights into the tasks people perform outside enterprise-level processes. (Signavio partner FortressIQ do this really well!) |
| Data mining | Analyzing large amounts of data to uncover patterns. Data mining is a technique used in process and task mining. |
| AI and machine learning | Artificial intelligence (AI) is the use of technology to mimic human intelligence. Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn from experience. This technology can be combined with process mining to create self-optimizing processes. |
| RPA (robotic process automation) | The use of software to perform repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions. It can be used to streamline processes and free people from more mundane tasks, but it is important to understand and optimize processes before introducing automation. Automating “broken processes” will limit the value RPA can offer. |
How has process mining become critical to modern enterprises?
Process mining started gaining traction about a decade ago. In 2009 a task force was established and in 2011 “the father of process mining,” Professor Wil van der Aalst, published his first book on the subject. Since then businesses have steadily become more reliant on digital technology to support or even completely automate processes. This digitization of modern enterprises has exponentially increased the data we have available and by extension the value we can extract from that treasure trove of data using process mining.
In addition to the increase in data, cloud computing has made process mining more accessible, empowering more businesses to use data to drive decisions. Using process mining to support data-driven decisions is a natural next step for modern enterprises.
Why should companies use process mining?
If your business already has process maps and documentation, you might wonder, “Why do process mining at all?” The answer is that process mining reveals the difference between what should be happening and what is happening. Businesses are often surprised at how visible their processes become when they use process mining — and what that visibility reveals about the mismatch between ‘as-is’ and ‘should-be.’ Even manual processes leave digital traces that can be eye-opening.
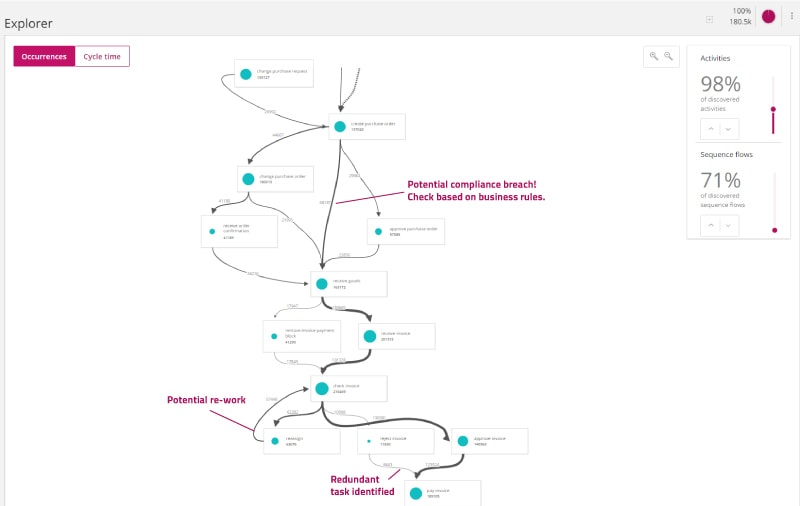
The reality is that the old way of value or process mapping relied on estimates and could “inadvertently represent the biases and misunderstandings of their creators” as Jung Paik and John Silver so tactfully put it in their article on mining for value with intelligent process analytics. They go on to say: “Process mining solves several major challenges. It brings speed, analytical power, and fact-based rigor to the problem of uncovering the sources of waste, inefficiency, and lost value in business operations.”
What can process mining improve?
Process mining software can help improve business performance and help organizations decrease costs and increase productivity by identifying the root causes of poorly performing processes, detecting and visualizing compliance violations, monitoring processes, and anticipating problems. The benefits are widespread, but can be particularly impactful for fundamental processes like order-to-cash and procure-to-pay.
In fact, one Signavio customer was able to cut their P2P cycle down by 80%, meaning they were able to secure a range of high-technology projects that required an agile approach to payments.
The valuable insights process mining techniques can deliver empower businesses to improve compliance via conformance checking, streamline processes and transform into resilient, adaptable organizations.
Discover more about the benefits of process mining with your
How does process mining improve the customer journey?
Process mining can be applied to customer journey mapping to connect the dots between your customer journey and the people, processes, decisions and IT systems that drive it. This visibility provides businesses with a better understanding of how internal processes impact customer experience. With this customer-centric view, you can improve processes to build a seamless customer journey and uncover new opportunities to delight customers along the way.
In industries where customer engagement is paramount, using insights gained via process mining to enhance customer experience can be a significant competitive advantage. To take just one example, we can look at the role played by customer experience excellence as a strategic differentiator for telecom companies.
When should you use process mining?
Companies use process mining to discover where and how value is created within their business. Process mining helps answer the types of questions that arise in day-to-day operations:
- Why was this customer invoice sent out incorrectly?
- Why did a group of customers in this area receive their orders two weeks late?
- Why isn’t the figure for “number of products sold” the same as the figure for “number of products shipped?”
Process mining might start with these more immediate questions, but it offers long-term benefits. Being able to visualize the inner workings of your business builds operational resilience by helping you anticipate problems, adapt quickly and see the impact of those changes. In recent years, we’ve seen banks and financial institutions, the hospitality industry and the telecommunications industry use process mining to navigate major shifts in how they operate. These examples can serve as a roadmap as businesses look to navigate the new normal and become stronger and more resilient after the pandemic.
Four steps to launch a successful process mining initiative
Process mining works by analyzing data to give you a picture of how your processes currently work and providing you with the information you need to make them better.
- Define your scope. Bring stakeholders together to agree upon the project objective, process and data requirements. Remember you can change and refine these as you go.
- Gather your data. Process owners often dread this step, but the right data mining tools make it relatively easy — you won’t be manually collecting reports. In almost all cases, you will connect the process mining tool to your systems using a standard software connector.
- Generate your insights. This is the exciting part when you see a process model based on your data and can start to analyze what is really happening at each step.
- Improve and measure your results. Now you can establish core process performance metrics and start to make data-driven changes.
Learn more about each phase in this in-depth white paper:

